Detect Surface And Subsurface Issues Easily
Through expert Magnetic Particle inspection by a skilled inspector, GIT Services will help you identify potential issues with your materials.
Our Industries Served Include:
- Petrochemical & Refinery
- Fossil Power
- Nuclear Power
- Oil & Gas
- Aerospace
- Industrial
- Pulp Paper
- Infrastructure
- Above Ground Storage Tanks
- Fabrication
Call or email today to learn more about Magnetic Particle Inspections.

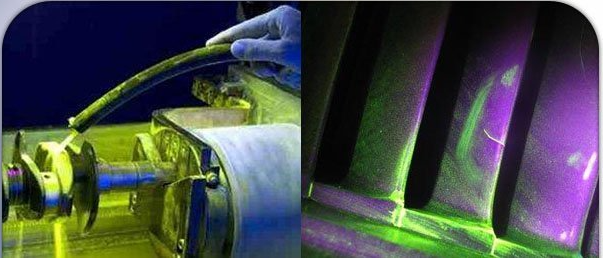
Magnetic particle inspection (MPI) is used for the detection of surface and near-surface flaws in ferromagnetic materials. A magnetic field is applied to the specimen, either locally or overall, using a permanent magnet, electromagnet, flexible cables or hand-held prods. If the material is sound, most of the magnetic flux is concentrated below the material's surface. However, if a flaw is present, such that it interacts with the magnetic field, the flux is distorted locally and 'leaks' from the surface of the specimen in the region of the flaw.
Fine magnetic particles, applied to the surface of the specimen, are attracted to the area of flux leakage, creating a visible indication of the flaw.
Magnetic Particle Inspection is a non-destructive testing method used for defect detection.
RMPI is a fast and relatively easy to apply and part surface preparation is not as critical as it is for some other NDT methods. These characteristics make MPI one of the most widely utilized non-destructive testing methods.
MPI uses magnetic fields and small magnetic particles, such as iron filings to detect flaws in components. Magnetic Particle Testing is a relatively easy and simple test method that can be applied at various stages of manufacture and processing operations.
The objective of Magnetic Particle Testing is to insure product reliability by providing means of:
- Obtaining a visual image of an indication on the surface of a material.
- Disclosing the nature of discontinuities without impairing the material.
- Separating acceptable and unacceptable material in accordance with predetermined standards.
